- BY braincandy
- POSTED IN Website Design & Development
- WITH 0 COMMENTS
- PERMALINK
- STANDARD POST TYPE


Security is an important aspect of anything. In this cyber age when the whole world is riding on the digital wave, the vulnerability of the digital applications in that wave is also increasing. The invention of different worms & viruses along with a booming number of hacking techniques has indeed made the security of enterprise mobile apps very shaky. The valuable and confidential data are always in the danger zone with a compromisable security framework. It is not paranoia but a cautionary tale of the current cyber globe. But it is not a totally gone out of the hand matter. Vigilant levels of precautions can insure these mobile applications from harmful cyber attacks. There are certain 5 ways by which security lapses in the mobile apps can be averted and eventually, make them strong. These are, in reality, some focus areas where the security can be tightened considerably to make the overall app secured. By deploying specialist for each of these areas can make the mobile app secured and the data failsafe.
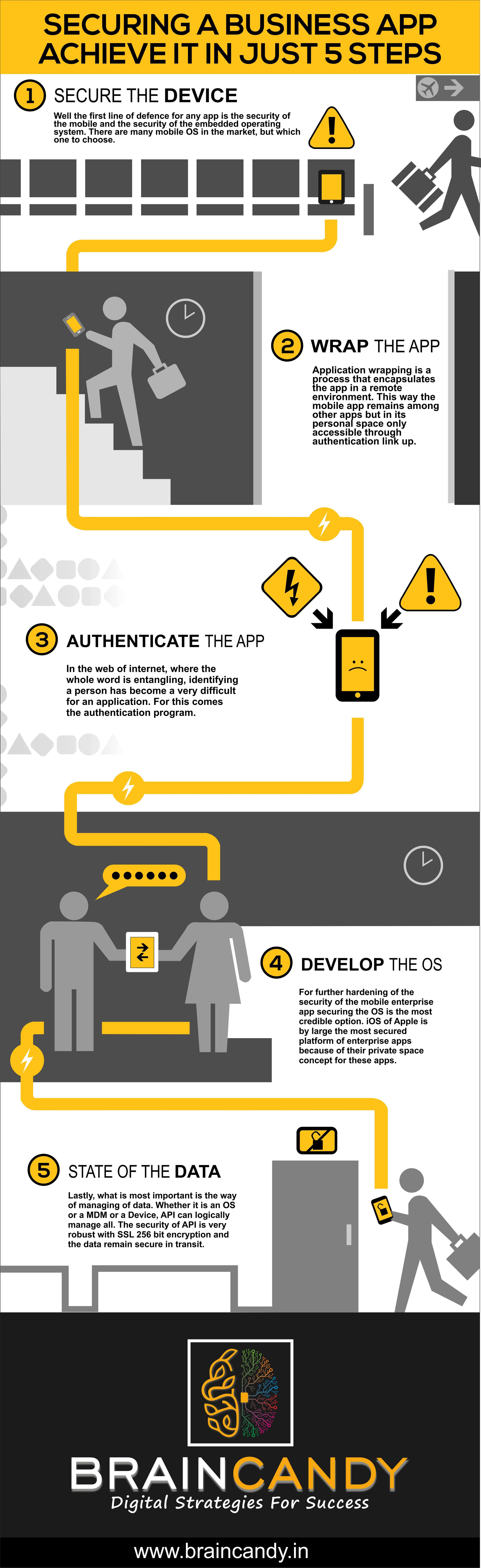
- Secure the Device – Well the first line of defence for any app is the security of the mobile and the security of the embedded operating system. There are many mobile OS in the market, but which one to choose. For enterprise mobile app Apple’s iOS is the first choice because it is much secured and has a strict enforcement policy. Due to these there is a restriction in installing apps without proper background. But there is a loop hole that comes in time of iOS updates. This hole can be corked by using Mobile Device Management (MDM) services from providers like MobileIron, Good Technology etc. One can also build their own manage program by Exchange ActiveSync Protocol from Microsoft created with bring-your-own-device program, but its effectiveness is lower than the exclusive vendors. The next comes Android, more feasible than Apple devices. With proper conduct with Google the Android for Work (A4W) version of the OS can be applied to the device. This not only separates personal apps from professional ones but also gives security to the enterprise data. All of these give the app its base layer of security.
- Wrap the App – Application wrapping is a process that encapsulates the app in a remote environment. This way the mobile app remains among other apps but in its personal space only accessible through authentication link up. Most of the MDM provides app wrapping and even Apple iOS supports it. The process is a non-coded one and is used for reporting app specific problems. Wrapping gives a good protection from unwanted cyber inbound.
- Authenticate the App – In the web of internet, where the whole word is entangling, identifying a person has become a very difficult for an application. For this comes the authentication program. The security of an enterprise app access is based on Single Sign On (SSO) portal constructed with a VPN and SAML (a security assertion mark up language) on a MDM. This will give the organisation monopoly on the access of the app thus securing its sensitive data. But with the aggressive and astute cyber crime ascension, single authentication is no way foolproof. To make authentication failsafe two tier identification program is required like OAuth 2.0.
- Develop the OS – For further hardening of the security of the mobile enterprise app securing the OS is the most credible option. iOS of Apple is by large the most secured platform of enterprise apps because of their private space concept for these apps. The Apple commercial tools give analytic reports of the security and other aspect of the app and also the well covered strict enforcement policy. In case of Google the concept of enterprise space came a bit late but it is not incompetent. The A4W consciously and securely separates the personal apps from professional apps.
- State of the Data – Lastly, what is most important is the way of managing of data. Whether it is an OS or a MDM or a Device, API can logically manage all. The security of API is very robust with SSL 256 bit encryption and the data remain secure in transit. Data in rest is more complicated because the data is stored in device. For this authentication and setting limitation in memory is the best way.